Exchange-traded funds, commonly known as ETFs, are a popular investment vehicle in the stock market. ETFs are baskets of securities, such as stocks or bonds, traded on stock exchanges like individual stocks. As a result, they offer investors the benefits of both mutual funds and individual stocks, with a lower expense ratio than traditional mutual funds and the ability to buy and sell throughout the trading day.
Investing in ETFs is a relatively simple process. Investors can purchase shares of an ETF through a broker, just like they would for individual stocks. However, ETFs are traded on major stock exchanges, so an investor must have a brokerage account and sufficient funds to invest in the ETF.
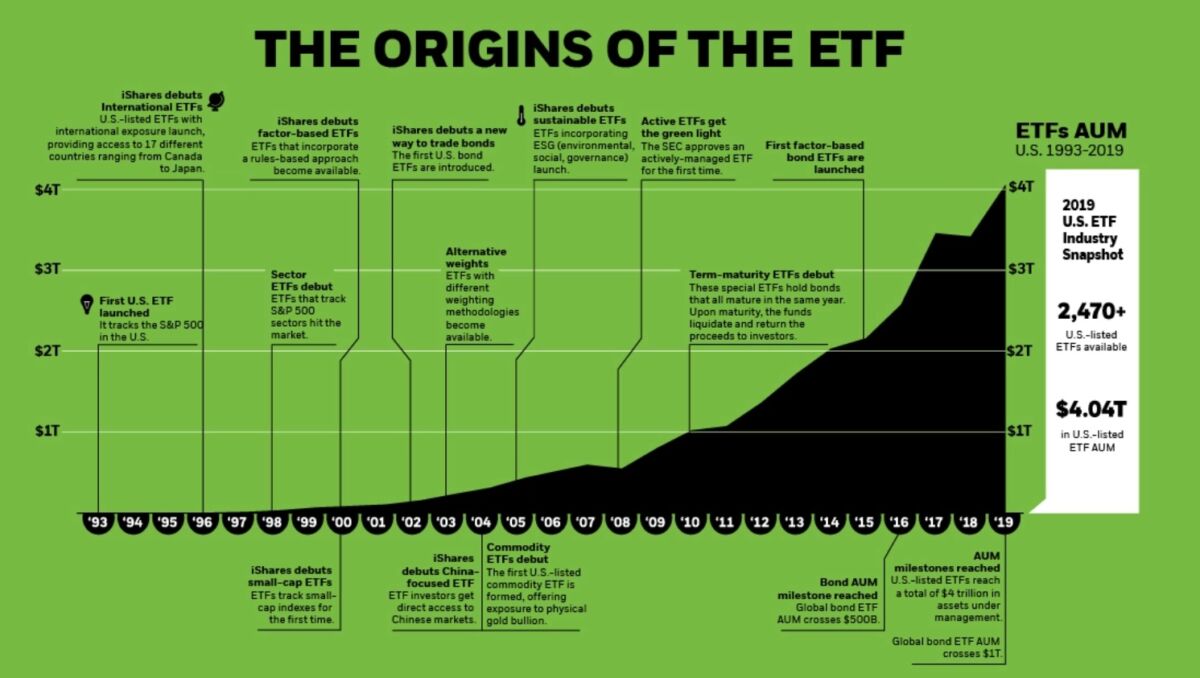
Origins of ETF, source: visualcapitalist.com
Benefits of ETFs
One of the primary advantages of investing in ETFs is their diversification. ETFs hold a variety of securities, which helps spread out an investor’s risk. For example, an ETF that tracks the S&P 500 index would provide exposure to 500 large-cap stocks in different sectors. This diversification can mitigate the risks of investing in individual stocks or bonds.
ETFs are also known for their low costs. Unlike mutual funds, which can have high management fees and other expenses, ETFs typically have much lower expense ratios. This is because ETFs are passively managed and designed to track a specific index or benchmark. As a result, there are fewer expenses associated with researching and analyzing individual stocks.
Another benefit of ETFs is their flexibility. Investors can trade ETFs throughout the trading day, just like individual stocks. This means that investors can buy or sell shares anytime during market hours rather than waiting for the end of the trading day. This flexibility also allows investors to use trading strategies, such as limit orders and stop-loss orders, to manage their investment risks.
More to read: What is Enterprise Value?
Many types of ETFs are available in the stock market, each with its investment strategy. Some ETFs are designed to track broad market indexes, such as the S&P 500 or the Dow Jones Industrial Average. Other ETFs may focus on specific sectors, such as technology or energy. Finally, some ETFs track specific commodities, such as gold or oil.
Investors can also choose between equity and fixed-income ETFs. Equity ETFs hold stocks, while fixed-income ETFs hold bonds. As a result, equity ETFs are typically more volatile than fixed-income ETFs but offer greater potential returns. On the other hand, fixed-income ETFs are less volatile but provide more stability and income.
You may also like: How to best invest cash?
Investing in ETFs does have some risks. Although ETFs offer the diversification, they can still be affected by market volatility, economic downturns, and other risks associated with investing in the stock market. In addition, some ETFs may have higher expense ratios than others, so investors should carefully research the costs associated with each ETF before investing.
In summary, ETFs are a popular investment vehicle in the stock market that offers diversification, low costs, flexibility, and various investment strategies. Investing in ETFs is relatively simple and can be done through a brokerage account. However, investors should carefully research the costs and risks associated with each ETF before investing.
Drawbacks of ETFs
While ETFs can offer many benefits to investors, they also come with potential drawbacks such as limited control, fees, and overlapping holdings. It’s important to understand these risks before investing in an ETF and to carefully evaluate any investment decision based on your individual investment goals and risk tolerance.
Limited Control: When you invest in an ETF, you are buying a bundle of securities that are chosen by the ETF manager.
Fees: Like any investment, ETFs come with fees. The management fee and other fees, can be relatively low for some ETFs, but it can still eat into your returns over time.
Overlapping Holdings: Some ETFs may hold many of the same securities as other ETFs, which can lead to overlapping holdings and reduce the diversification benefits of holding multiple ETFs.
Various ETF portfolios
There are many different types of ETF portfolios available to investors, each with its investment strategy and level of risk. Here are some examples of ETF portfolios that investors might consider:
- Broad market ETF portfolio: This portfolio consists of ETFs that track broad market indexes, such as the S&P 500 or the Russell 2000. The goal of this portfolio is to provide exposure to a diverse range of stocks across different sectors, intending to generate long-term growth.
- Sector-specific ETF portfolio: This portfolio consists of ETFs that focus on a specific sector, such as technology, healthcare, or energy. This portfolio aims to provide exposure to companies within a particular industry to capitalize on growth opportunities within that sector.
Also interesting: Wall Street opens with a bullish surge; stocks erase daily losses
- Global ETF portfolio: This portfolio consists of ETFs that provide exposure to stocks from around the world, including developed and emerging markets. This portfolio aims to diversify across different regions and currencies to generate long-term growth.
- Dividend ETF portfolio: This portfolio focuses on companies that pay dividends to their shareholders. The goal of this portfolio is to generate income through regular dividend payments and long-term growth.
- Bond ETF portfolio: This portfolio includes ETFs that track various fixed-income securities, such as government bonds, corporate bonds, or municipal bonds. This portfolio’s goal is to diversify different types of bonds to generate income and preserve capital.
In conclusion, ETFs have their specific advantages and risks, and it is up to any trader to do their own research before investing into a portfolio. This might be the right way to start investing for many, as ETFs offer a lot of different options.











Comments
Post has no comment yet.