With CFDs, you can leverage shares worth $ 20-30,000, even though your collateral is $ 10,000. This is called leverage. However, a greater risk is involved because if your $ 30k investment fell by 33%, you would lose your $ 10k collateral, respectively (because its calculated from your leveraged position). Then you would be called for a margin call to inject additional capital. Otherwise, your broker would close your position because you would not have enough funds in your account.
The same goes for the other side. So be careful about this. You can read more details about leverage, margins, and margin calls here.
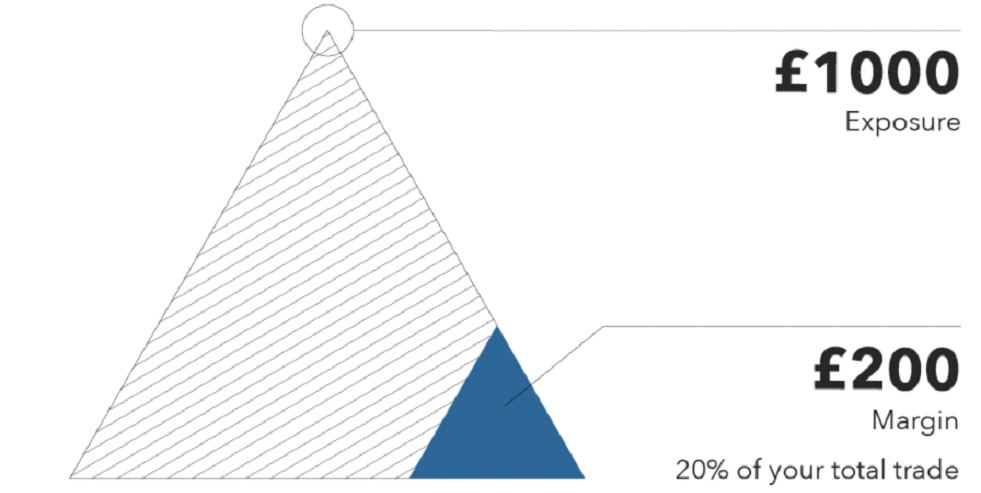
Source: https://www.ig.com/ae/trading-strategies/what-is-margin-in-trading–200224
The most appropriate and safest form if you are a beginner is to focus purely on stocks without using leverage. If you already have experience, you can also embark on derivatives, but there are significantly higher risks and potential. You pay only a minimal fee and do not pay any holding fees to purchase stock from many brokers. For some derivatives (CFDs), you pay a fee every day (overnight swap), depending on your position size.
You do not pay anything for options other than entry and exit fees, but here it should be bear in mind that options are derivatives that decline over time. I do not recommend going into this segment without studying option strategies. However, in the case of advanced knowledge, options are an excellent tool for hedging or speculation. Options are gaining in attractiveness mainly in the USA and Europe, as evidenced by the chart below, which clearly shows that people are increasingly trading through these popular derivatives. The options market also has its secrets and may indicate significant speculative activity. Several “options indicators” can be very useful from a macro perspective and help us define what is happening in the market and be a leading / contrarian indicator.
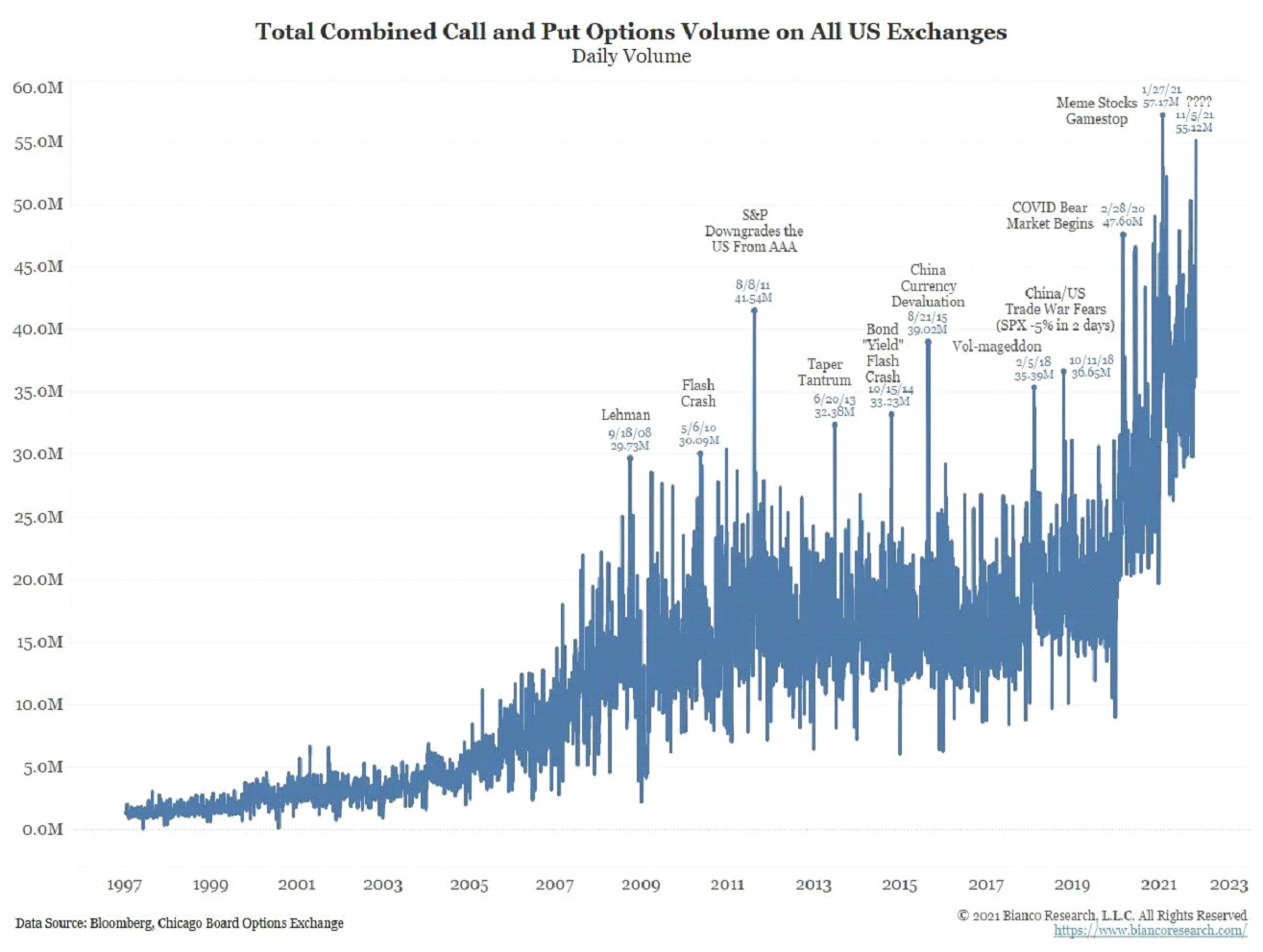
Source: Bloomberg, Chicago Board Options Exchange


Comments
Post has no comment yet.