A share/stock is a type of security representing a particular share in the company’s ownership interest. The shares or stocks are traded on the stock market on various exchanges (American, European, Asian, etc.) or the OTC market. Investors can buy them through online brokers, banks, or the stock exchange. Voting rights at shareholders’ meetings are also associated with share ownership. Companies have the opportunity to issue shares on the primary market, which means that at this stage, they obtain capital from investors. In the secondary market, shares/bonds are traded between market participants.
Not always if you own shares, you have the opportunity to vote at the general meeting. Only if you buy a “common stock.” Preferred stocks usually do not have voting rights. Still, investors participate more in the company’s growth and, at the same time, receive a dividend rather than common shareholders and also have a priority position if the company awaits liquidation (share in assets). However, it can also vary depending on the type of event. Some companies prefer the issuance approach to a large extent only “preferred stocks” because they allow the company’s management to be fired by shareholders. Or they just don’t want shareholders to push them into business.
We often see the stock’s name with the letter A, C, etc. (written at the end of the stock). These shares differ in voting rights, the amount of the dividend, and many times the price. For example, I present Google’s stocks (Alphabet) on the German market. However, it always depends on the policy of the company.
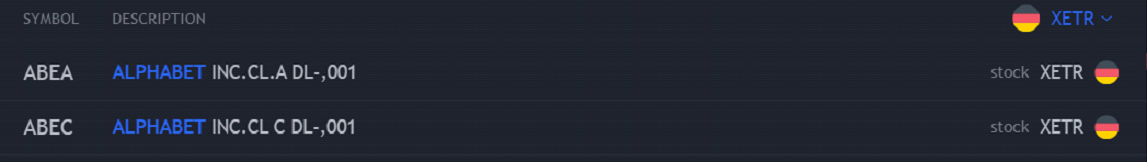
Source: Tradingview
Bonds differ from stocks in many ways. E.g., it is much more conservative security that provides less yield but is not subject to such volatility (price fluctuations as a stock). Honestly, bonds are a chapter itself, but they can also be very volatile. Remember that bonds with investment grades and short-term maturity tend to be less volatile. However, bonds with long-term maturities tend to be very volatile, sometimes the same as high beta stocks. Another key difference is that in the event of bankruptcy, the bondholders have priority over the shareholders in the final balance. According to the law, bondholders will be satisfied before the shareholders even if the company is in bankruptcy and is forced to sell its assets. Sometimes, they are likely to return only part of their investment, and shareholders are worse off. But not in all cases. When buying bonds, some kinds of bonds are not covered by the company’s assets.
Essential criteria for a bond are the price at which it is traded and the yield. And also a duration. Bonds are a very important part of the capital market, and their issues and definitions can be described in hours.


Comments
Post has no comment yet.