Important points about Silicon Valley Bank
Despite all regulations, the system was unable to prevent the first major unofficial bankruptcy of one of the largest banks in the United States, specifically in the TOP 20 in terms of assets totalling over $200 billions. There are two primary explanations.
First is the extremely poor management of SVB, as its interest rate risks were not hedged. The second is also related to management: the loosening phase, which led to the IPO and valuations frenzy, has ended, but the company has taken no steps to deal with it.
Read also: What is portfolio diversification?
In the analysis, we will attempt to discuss every detail hidden behind the wall, explain how it is even possible, and reveal what actually occurred and why. Since the quality of loans is significantly higher than it was prior to 2008, the system is currently much more secure than it was prior to that year.
This is not a 2008 event, but it could spark a significant psychological effect, causing bank deposits to suffer. The banks with similar policies and unhedged portfolios may experience similar outcomes.
How the banks work – the secret is in the balance sheet
We consider it crucial to comprehend how banks actually operate and to apply these principles to the SVB Financial Group, which is more risk-tolerant because it primarily provides funding to companies seeking venture capital. The bank’s balance sheet differs significantly from that of non-banking companies. The bank views the client’s deposits as a liability and the loans as an asset.
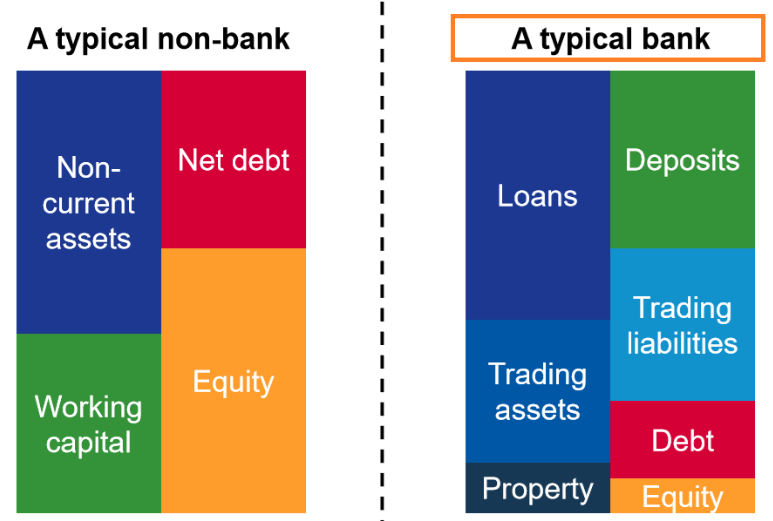
Financial Statements for Banks, source: Corporate Finance Institute
Simply put, as client deposits increased, the bank must acquire assets. The explanation is straightforward. The bank is responsible for ensuring that it has sufficient liquidity to meet current and future withdrawal requests from customers. But one way, is through loans. It impacts the NII, or net interest income, which is the income earned by banks through the spread between interest on savings accounts and interest on loans.
We also informed about: Gold and silver work as safe havens while fear spreads all over
If the bank is unable to deliver as many loans as possible, liquid assets such as cash, reserves, and bonds should be allocated. One method of utilizing such deposits is to hold them as excess reserves at the Fed.
Additionally, there is the option of increasing trading assets, or purchasing bonds with strong credit ratings and short- to medium-term maturities. It can be accomplished in a number of ways, but the most reliable method is to purchase safe US Treasury securities and agency-issued MBS.
Extraordinary loosening policy and its implications on SVB’s balance sheet
The majority of SVB Financial Group’s clientele are associated with venture capital. They provide loans to early-stage startups, life sciences, as well as direct financing services to venture capital firms and their portfolio firms. Additionally, the same services are provided to private equity.
The issue is that market demand for such capital and loans from SVB Financial Group was substantial in 2020-2022. There was a boom, and every start-up traded at ludicrous multiples and valuations. This is supported by a record-breaking IPO and one of the largest valuations in decades.
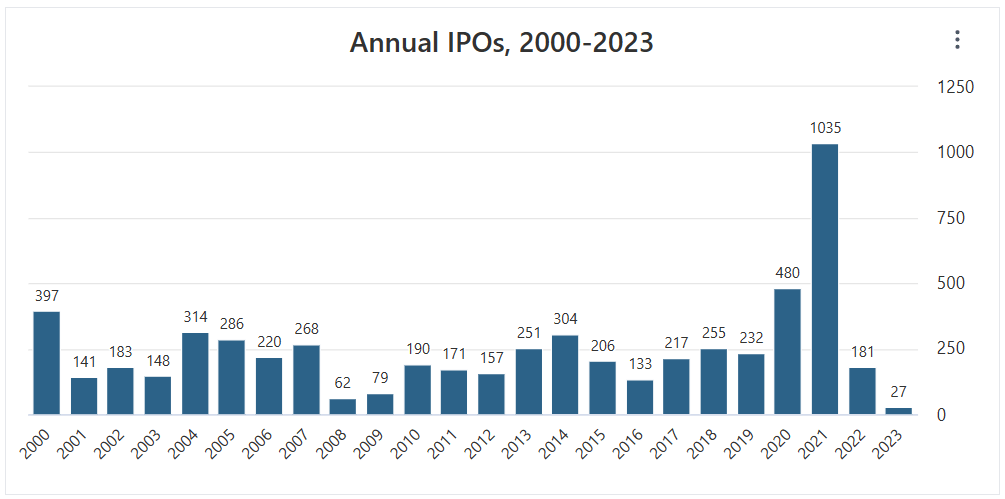
Record IPOs in 2020-2021, source: stockanalysis.com
One of the most significant causes was the dramatic tightening of monetary and fiscal policy that began in 2022. We should not be surprised by the “low” level of IPO activity in 2022. There is a demand for IPOs when monetary policy is significantly loosened, because there is an abundance of cash and liquidity in the marketplace.
Once it begins to decline, as it has in 2022 and 2023, the problems will occur, valuations will normalize, and IPO activity will return to normal, or levels below standard deviations. The reason we mention this is due to the rise in deposits of these companies. Due to the bank’s clientele, the Silicon Valley Bank serves a large number of technology companies and start-ups with corporate accounts. As a result of the success of these companies in 2020 and 2021, its deposits increased significantly.
ZIM is up more than 30% since our last research: Stock Research: ZIM – a new hidden gem?
The SVB balance sheet increased from approximately $100 billions in 3Q2020 to over $210 billions in 1Q2022. During a period of loosening monetary policy, nearly every business and startup had a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity for nearly free funding. The number of deposits increased significantly as a result of a large number of companies’ IPO and stock offering proceeds.
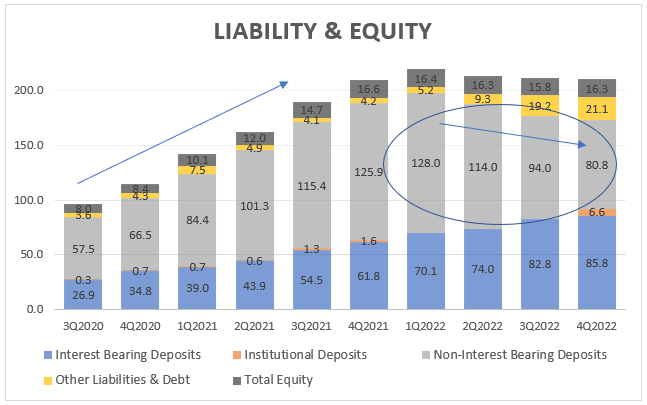
SVB Financial Group – Liability & Equity, source: Investro analytics team, data from Seeking Alpha
As soon as the Fed and global central banks began to tighten, the story ended. The majority of start-ups and post-IPO businesses have negative earnings per share and negative cash flow, which is eroding their cash position. Moreover, funding is not as accessible and inexpensive as it was two years ago.
When the company reported three consecutive quarters of declining Non-Interest Bearing Deposits (NIBD), the first red flag was raised . Although Interest Bearing Deposits (IBD) are increasing slightly from quarter to quarter, the increase is much slower than the decline in Non-Interest Bearing Deposits (NIBD). The decline in deposits is not simply an SVB Financial Group pattern, but a natural and logical consequence of the significant withdrawal of market liquidity.
Learn from the best: How is Warren Buffett investing – top picks of legendary investor
According to FRED, all commercial banks are experiencing a decline in deposits for what we believe is one primary reason. The rates on deposits (savings) are too low, and investments or cash parking in the US Treasury are far more attractive and secure than parking in banking products. Customers would rather invest in U.S. Treasuries than wait for banks to increase the interest rates on savings accounts. Consequently, client deposits should decline.
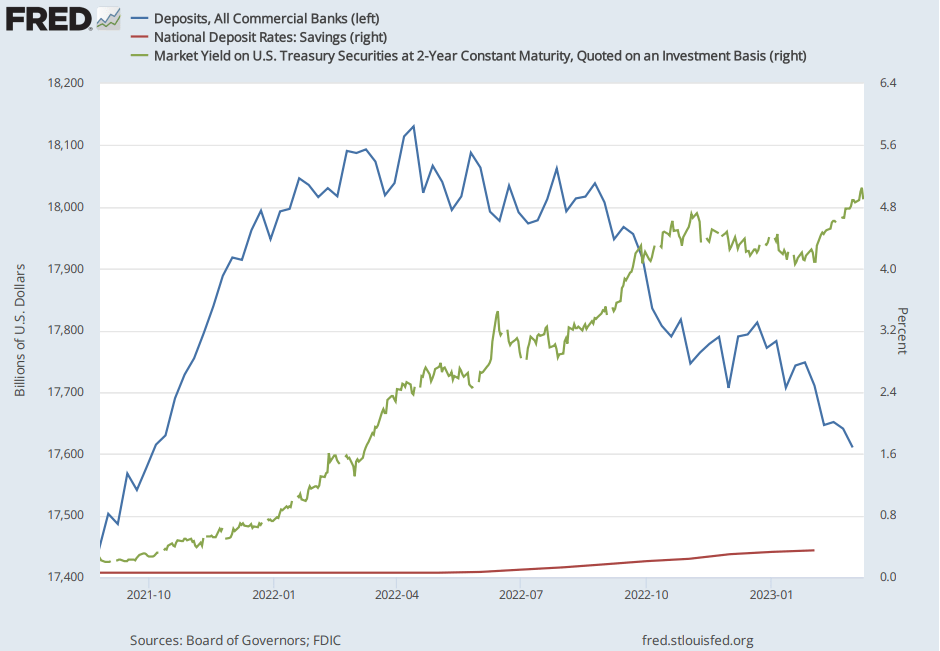
Deposits, savings rate and treasury yields, source: FRED, Board of Governors, FDIC
Review the liability and equity chart once more. This is the reason why NIBD are decreasing so rapidly globally. And specifically for the SVB, another reason is that the vast majority of start-ups are burning through their cash.
There may be a solution to the problem. Consider the expanding prevalence of IBD. If the group were able to increase its deposit rate for savings accounts, there would be no significant decrease in deposits, and the group would not be forced to sell a portion of its asset portfolio at a significant unrealized loss. Instead it could hold the bonds or MBS until maturity (thus all losses would be avoided). However this solution can be tricky.
The connection with assets
As mentioned in Basil III , there are certain requirements for what constitutes HQLA (high quality liquid assets). It can be cash, reserves, or bonds, as stated. However, the MBS and US Treasuries are included, so these assets could be considered HQLA. Examine the declining trend of these assets as well as the significant decline in cash below:
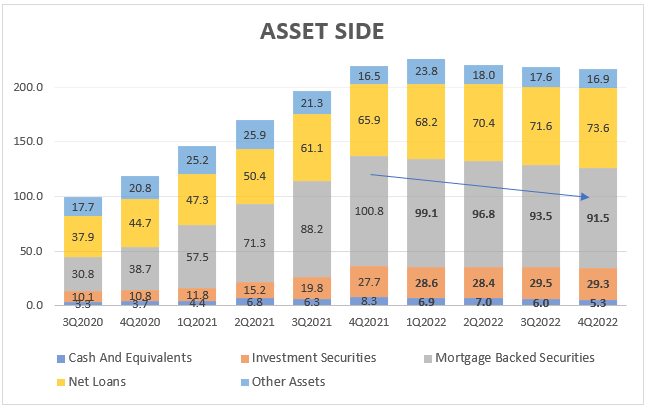
SVB Financial Group – Asset side, source: Investro analytics team, data from Seeking Alpha
According to the company’s filling for FY 2022, the securities can be classified as Available-For-Sale (AFS), totalling $26 billion or Held-To-Maturity (HTM). The composition of the portfolio carries a substantial proportion of risk, as it consists primarily of securities maturing within one to five years ($14.7 billions) and, secondarily, after ten years, totalling $7.2 billions.
We rated this stock very negatively: Norwegian Cruise: Stock dilution possible due to ruined balance sheet
A significant rise in yields (as a result of Fed monetary policy and actions) could result in significant losses if the position is not hedged. If positions are not hedged with derivatives, the company is exposed to substantial risk. This recently materialized. Unrealized losses for the AFS portfolio amount to $2.5 billion as of 4Q2022.
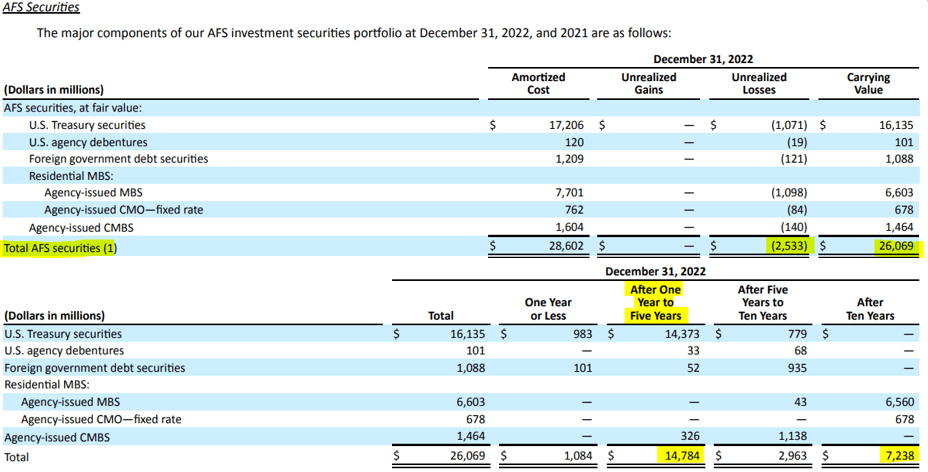
Unrealized loss and securities maturity in AFS portfolio, source: SVB, Investro analytics team via Form-10K, annual report
The second portfolio is known as Held-to-Maturity (HTM) and totals $91 billion at amortized costs, while its fair value is close to $76 billion after adjusting for $15 billions of unrealized losses. Again, the majority of the portfolio seems to be mature in ten years. For both portfolios, the unrealized loss exceeded $17 billion.
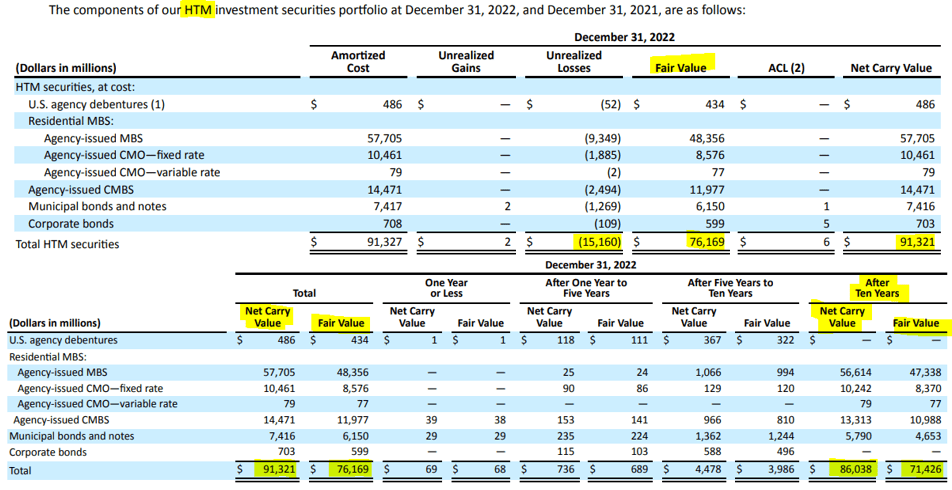
Unrealized loss and securities maturity in HTM portfolio, source: SVB, Investro analytics team via Form-10K, annual report
Tail-event, or what happened to Silicon Valley Bank?
As stated in the previous section, deposits had already declined in the previous quarters. However, the VC firms and other customers began to withdraw money from the bank accounts. As stated previously, providing funding to VC firms is risky. The clientele’s investment activity is declining because they are cash-burning and have less or, to be honest, no cheap access to funds.
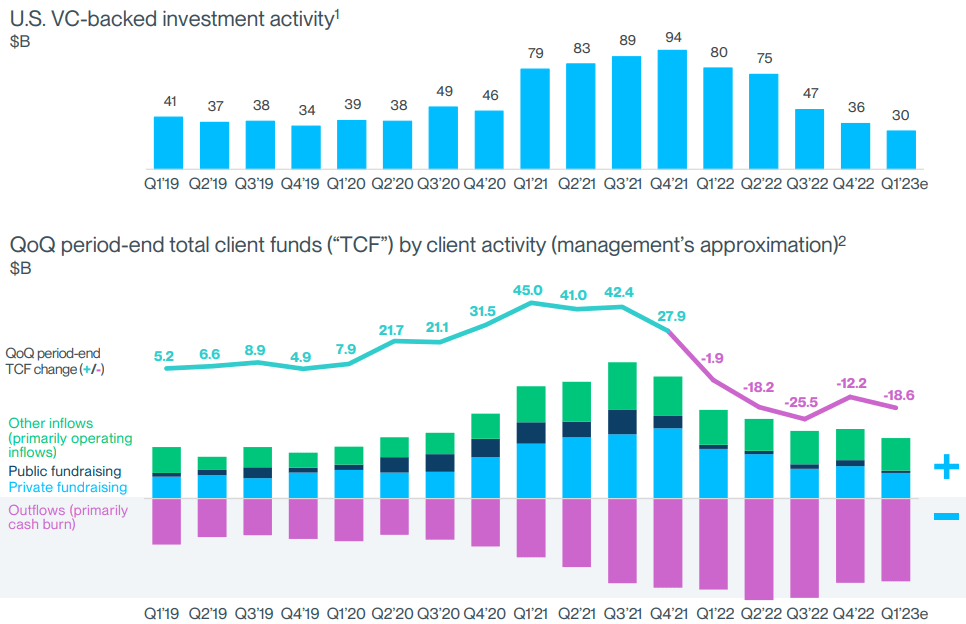
VC in troubles, cash burning, source: SVB Financial Group – presentation
The company’s asset side liquidity was insufficient, its cash position was weak, and the bank does not count on that. As reported by the company in its mid-Q1/2023 update:
“We have sold substantially all of our Available for Sale (AFS) securities portfolio with the intention of reinvesting the proceeds, and commenced an underwritten public offering, seeking to raise approximately $2.25 billion between common equity and mandatory convertible preferred shares. As a part of this capital raise, General Atlantic, a leading global growth equity fund and longstanding client of SVB, has committed to invest $500 million on the same economic terms as our common offering.”
The AFS portfolio was sold for $21 billions. Looking at the amortized costs of AFS’s $28 billion portfolio, we can assume that the loss has increased from -$2.5 billion to -$7 billion (at the time when US10Y Treasury yields were 4-4.1%). It depends on whether they sold the entire AFS portfolio. The unrealized loss in HTM portfolio would be considerably greater.
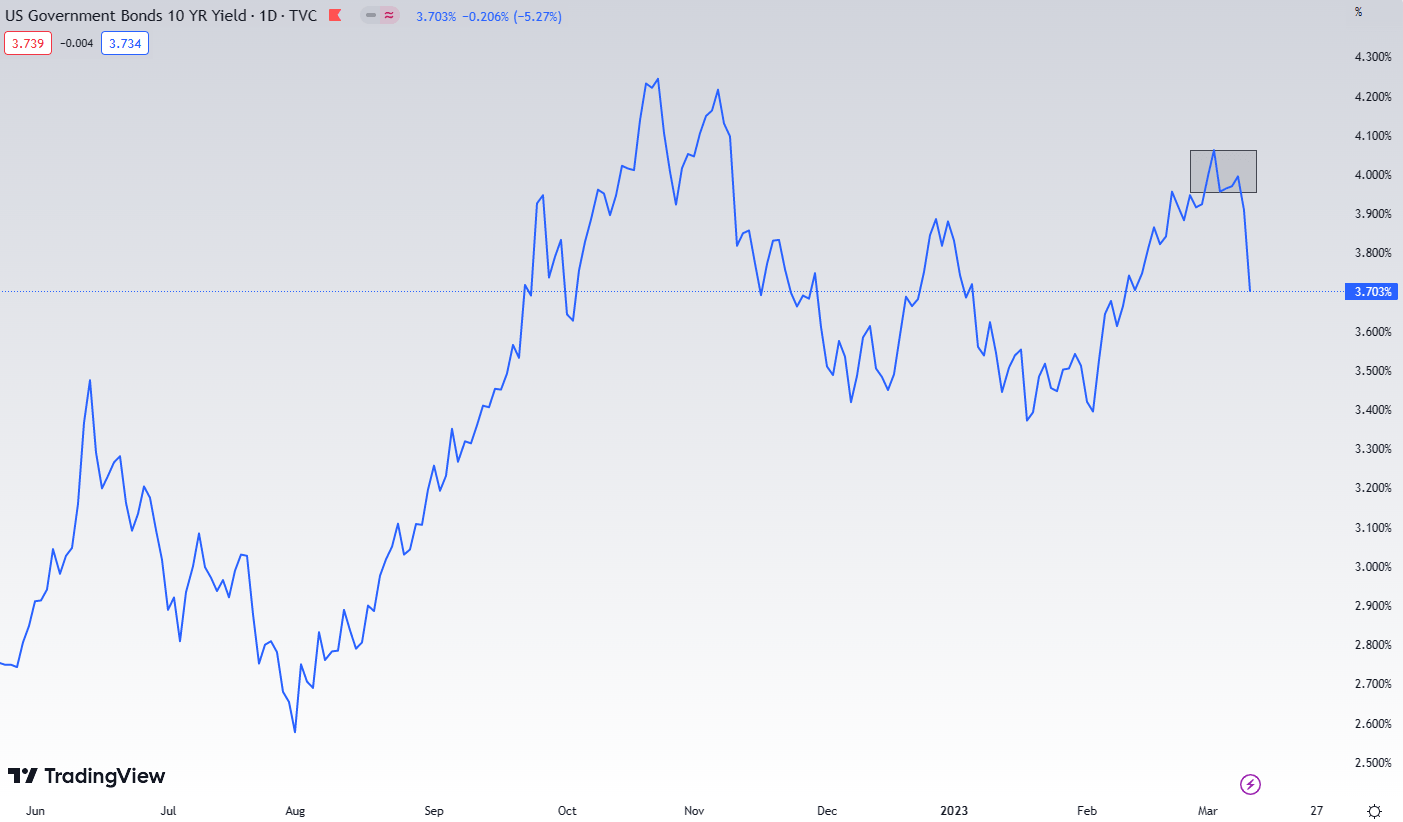
US 10Y Treasury yield, source: tradingview.com
Management mistake and further threats
As previously stated, the portfolio’s unrealized loss would not exist if it were held to maturity. The problem was that SVB Financial Group had liquidity and solvency issues as a result of a bank run in which numerous customers attempted to withdraw their deposits. It triggered liquidity issues, and the company attempted to resolve the issue by stock offering:
You may also like: Financial sector bleeds amid bank failures; who’s next to go bust?
“SVB Financial has failed in attempts to raise capital, and has started talks to sell itself, CNBC reported Friday, citing unnamed sources. The company has hired advisers to explore a potential sale, and large financial institutions have shown interest in a purchase,” CNBC’s David Faber said.
While the company reported healthy regulatory ratios at first glance, which could suggest a solid liquidity and solvency position relative to its risk assets, this is not entirely accurate.
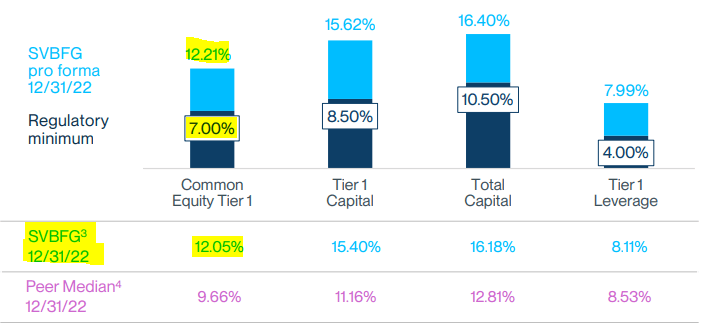
Crucial regulatory ratios SVB, source: SVB Financial Group – presentation
Observing the excellent chart from JPMAM, which also takes into account the impact of unrealized securities losses on capital ratios, it is evident that SVB would fall significantly short of regulatory requirements.
It is simply evident that the current situation is much more the result of poor management decisions than aggressive Fed tightening. One may be wondering why there is such a significant divergence between SVB and other banks. Other banks hedged their exposure to interest rate risk with derivatives. SVB did not.
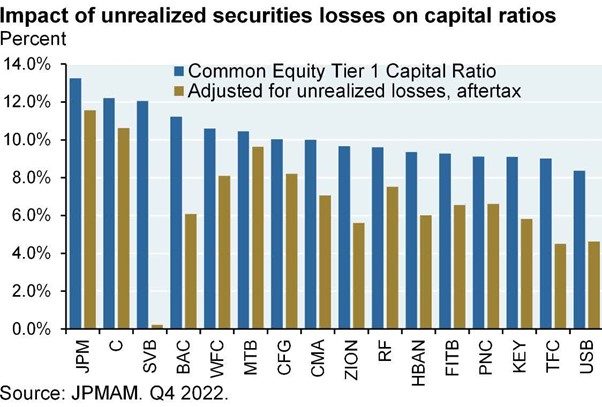
Impact of unrealized securities losses on capital ratios, source: JPMAM, Q4 2022
In the Q4 2022 investor presentation, it is stated that the hedge-adjusted portfolio duration is 5.6 years, which is identical to the duration of the traditional portfolio. In other words, no hedge and considerable moral hazard.
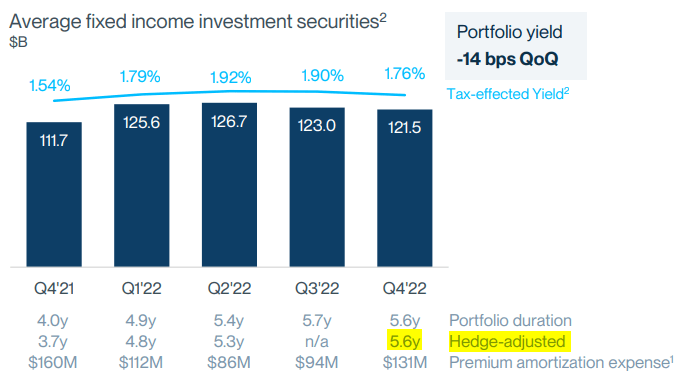
(Non)Hedge adjusted AFS portfolio, source: SVB Financial Group – Investor´s presentation
Moreover, do not forget that the management probably knew everything that was going to occur. As can be seen in the plot below, they sold a considerable amount of stock at the end of February.
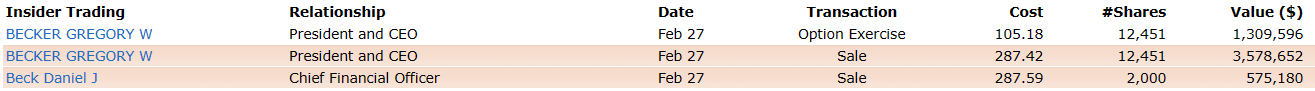
Insider Trading – SVB Financial Group, source: finviz.com
We will not speculate on who will come next. We are convinced, however, that this is not the case similar to that of 2008. Previously, the subprime mortgage crisis and the practice of providing mortgages to everyone out of greed caused a domino effect. To prevent such occurrences, significant and extensive regulations have been enacted since. Nonetheless, one similarity exists.
See our latest pick: Palantir Technologies: Profitability on the way in 2023
The psychological effect of bank customers can be quite potent and may result in vigorous withdrawal attempts, which should harm the banks in a comparable manner. Regional banks, which are less regulated than the most systemically significant banks, comprise the structure of the banks with the highest risk profile.
In addition, if a similar business model exists, it may be the source of the problem. If the bank run realized we need to focus on cash ratio. See the competitor´s cash ratios of other banks with tangible book value as % of balance sheet. The lower ratios, the worse. Some peers are in even worse conditions (in the current metric).
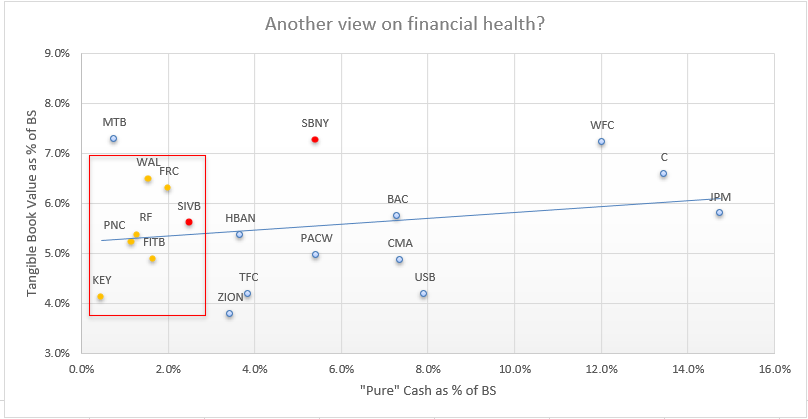
Pure Cash and Tangible ratio as a % of balance sheet, source: Investro analytics team
Conclusion – is bank run possible?
In the coming weeks, we’ll keep a close eye on the situation, and we’ll likely also examine banks in a similar position. Honestly, if the withdrawal mentality of customers persists, a run on the bank could pose significant systemic risks.
In contrast, the situation in 2008 was significantly worse and somewhat different. At the end, some of the big players will probably purchase the bank. As numerous banks are currently offering substantial discounts, we see a solid opportunity there, but we must emphasize that you do your own due diligence.










Comments
Post has no comment yet.