Here we are again. Banks are falling like dominoes, and market volatility has been massively elevated. In today’s banking climate, with more and more banks crashing upwards of 50%, it is important for us to bring you information regarding key doomsday terminology. You will probably hear a lot of these over the next few days, and it is key to know what is what.
Many analysts think the Fed is done with the tightening cycle as the next financial crisis has arrived. Let’s discuss some basic terms used in the trader’s jargon to describe the current situation.
What is a bank run?
A bank run occurs when a large number of depositors take their cash from a bank in a short time, typically out of worry for the bank’s solvency or liquidity. This might cause a lack of money at the bank, making it difficult for the institution to satisfy its commitments to depositors and other creditors. Under severe circumstances, a bank run may result in the institution’s bankruptcy or insolvency.
Many causes can provoke bank runs, including suspicions regarding the bank’s financial health, news of a significant economic crisis or political instability, or a rapid change in the economic climate. Moreover, bank runs can be contagious, moving from one institution to another and causing a broader financial crisis.
What is a bank contagion?
Bank contagion happens when financial troubles in one bank or financial institution spread to other financial institutions or banks, posing a systemic risk that threatens the stability of the whole financial system. For example, bank contagion can emerge when economic activities, such as interbank lending, trading of securities, or other financial derivatives, interconnect banks.
Also interesting: Nasdaq jumps up and down after US government announces bailout
A combination of causes, such as an abrupt shift in the economic climate, a significant economic crisis, or a shock to the financial system, can trigger bank contagion. It can also be caused by a lack of faith in the financial system, resulting in a domino effect when depositors shift their money from one bank to another.
What is a recession?
In simple terms, a recession is a period of economic downturn marked by a reduction in the gross domestic product (GDP). The most common indicator is a decrease of GDP over the last two consecutive quarters. It is often triggered by several causes, like employment, and trade, including a fall in consumer spending, company investment, and government spending.
National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) economists measure recessions by examining, among other indications, nonfarm payrolls, industrial production, and retail sales, going much beyond the simpler (but less accurate) two quarters of negative GDP metric.
What is a depression?
Bank run and bank contagion can also lead to widespread panic and financial crisis. Recession goes hand in hand as this is all tied together. On top of all this, recession can lead to financial depression.
A depression is a sustained and severe decline in economic activity. It may be characterized as an intense recession lasting at least three years or resulting in a fall of at least 10% in real GDP in a particular year. They are much more uncommon than recessions.
More to read: Financial sector bleeds amid bank failures; who’s next to go bust?
Since 1850, the US has had at least 34 recessions, such as the Great Recession of 2008-2009 as well as the recent covid recession of 2020. Yet, the US has only had one depression, that spanned from 1929 to 1939 and is recognized as the Great Depression.
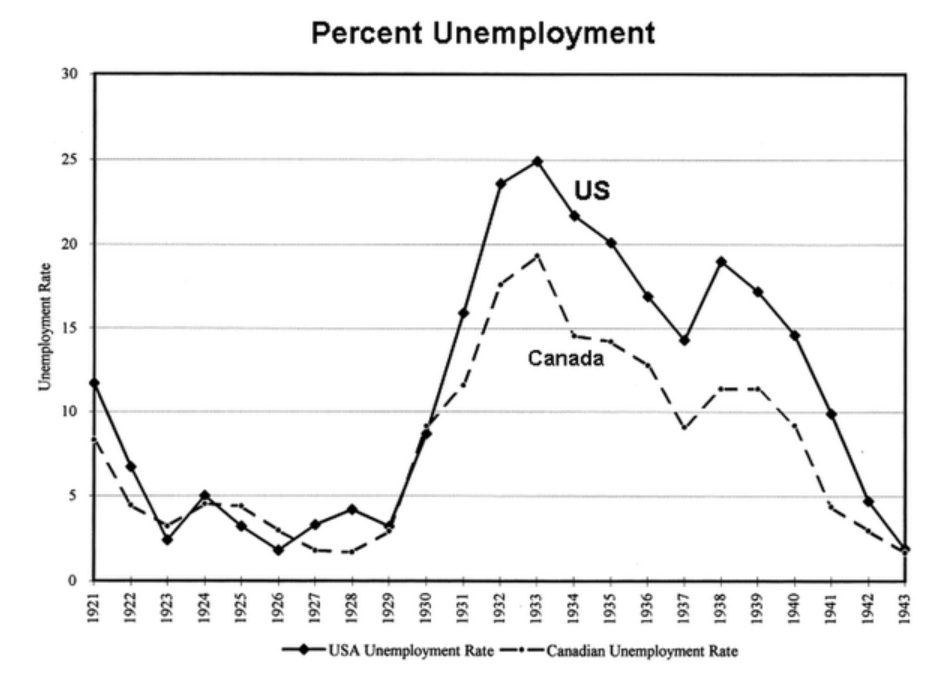
US vs Canada unemployment during the great depression chart, source: bigtrends
What is a financial crisis?
A financial crisis is a more severe kind of recession, marked by an abrupt and significant financial system disruption. A financial crisis may be triggered by a number of events, including a drastic decline in asset values, the fall of a large financial institution, or a severe credit crisis. Financial crises can have serious repercussions, including reduced credit availability, a fall in economic activity, and a substantial increase in unemployment.
Financial crises can also have long-term effects, such as a fall in the quality of life, a decline in economic growth, and a loss of faith in the financial system. In addition, financial crises may also have substantial political and social effects, such as a decline in public confidence in the government and an increase in political radicalism.
You may also read: Depegging of stablecoins – what does it mean and why is it happening?
Conclusion
In conclusion, bank runs, contagion, and financial crises are all tied to the financial system’s stability. Bank runs, and contagion can spark a financial crisis. There is a variety of other causes can also trigger it, therefore, understanding the origins and effects of these occurrences is crucial for policymakers, investors, and the general public.
It is important not to panic, and most of all educate yourself. Ultimately it is up to your knowledge to limit the risk of financial instability and safeguard your long-term economic health.











Comments
Post has no comment yet.